What's New in 4.4.4.Final
Docker Tools
Update of Docker Client
The level of the underlying com.spotify.docker.client plug-in used to access the Docker daemon has been upgraded to 3.6.8.
Run Image Network Support
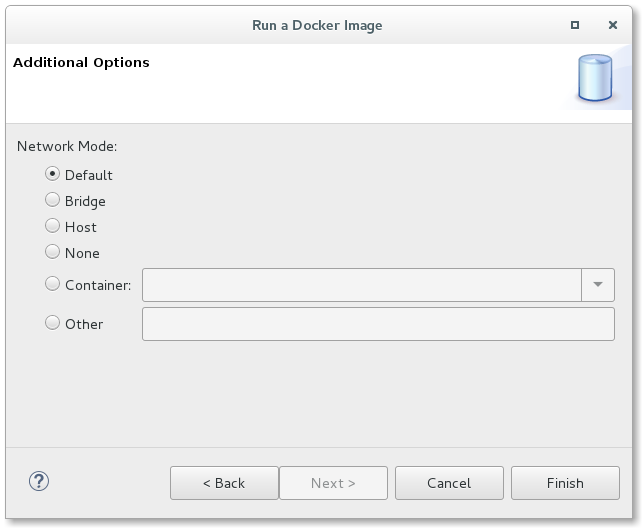
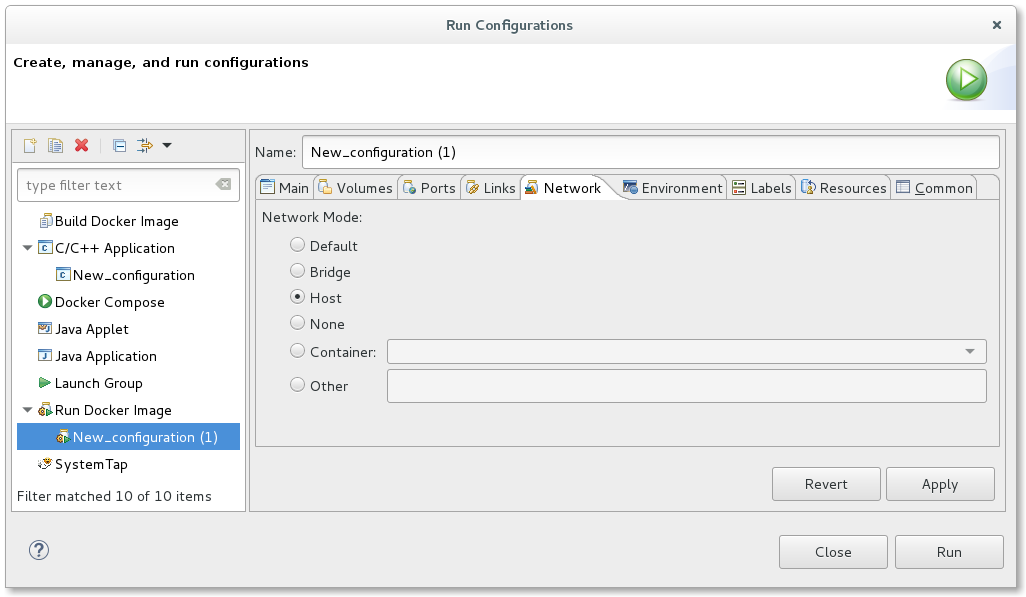
A new page has been added to the Docker Run Image Wizard and Docker Run Image Launch configuration that allows the end-user to specify the network mode to use. A user can choose from Default, Bridge, Host, None, Container, or Other. If Container is selected, the user must choose from an active Container to use the same network mode. If Other is specified, a named network can be specified.
Forge Tools
Forge Runtime updated to 3.6.1.Final
The included Forge runtime is now 3.6.1.Final. Read the official announcement here.
Hibernate Tools
Hibernate Runtime Provider Updates
The Hibernate 5.0 runtime provider now incorporates Hibernate Core version 5.0.12.Final and Hibernate Tools version 5.0.5.Final.
The Hibernate 5.1 runtime provider now incorporates Hibernate Core version 5.1.4.Final and Hibernate Tools version 5.1.3.Final.
The Hibernate 5.2 runtime provider now incorporates Hibernate Core version 5.2.8.Final and Hibernate Tools version 5.2.2.Final.
OpenShift
OpenShift Server Adapter enhanced flexibility
OpenShift server adapter is a great tool that allows developers to synchronize local changes in the Eclipse workspace with running pods in the OpenShift cluster. It also allows you to remote debug those pods when the server adapter is launched in Debug mode. The supported stacks are Java and NodeJS.
As pods are ephemeral OpenShift resources, the server adapter definition was based on an OpenShift service resource and the pods are then dynamically computed from the service selector.
This has a major drawback as it allows to use this feature only for pods that are part of a service, which may be logical for Web based applications as a route (and thus a service) is required in order to access the application.
So, it is now possible to create a server adapter from the following OpenShift resources:
-
service (as before)
-
deployment config
-
replication controller
-
pod
If a server adapter is created from a pod, it will be created from the associated OpenShift resource, in the preferred order:
-
service
-
deployment config
-
replication controller
As the OpenShift explorer used to display OpenShift resources that were linked to a service, it has been enhanced as well. It now displays resources linked to a deployment config or replication controller. Here is an example of a deployment with no service ie a deployment config:
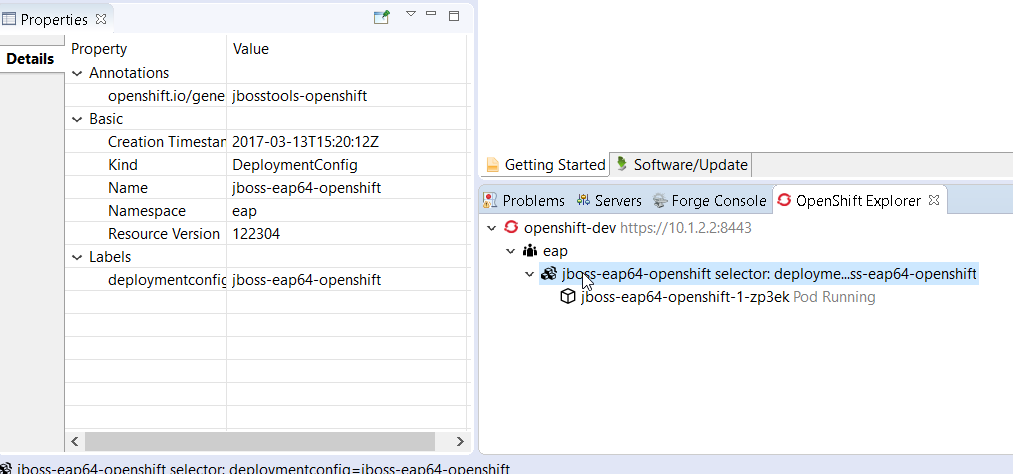
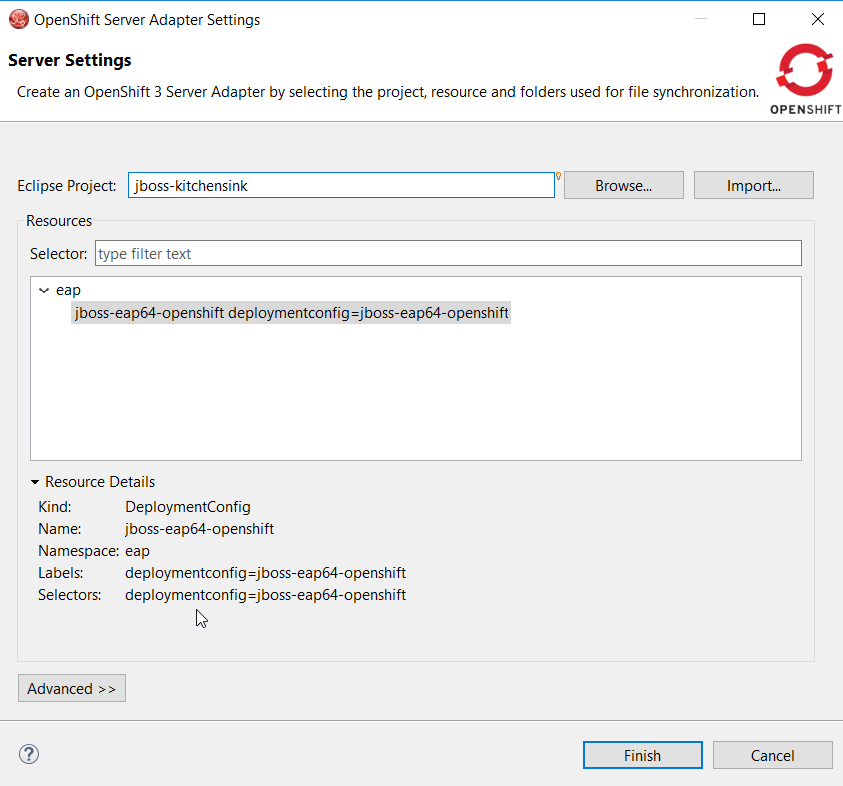
So, as an OpenShift server adapter can be created from different kind of resources, the kind of associated resource is displayed when creating the OpenShift server adapter:
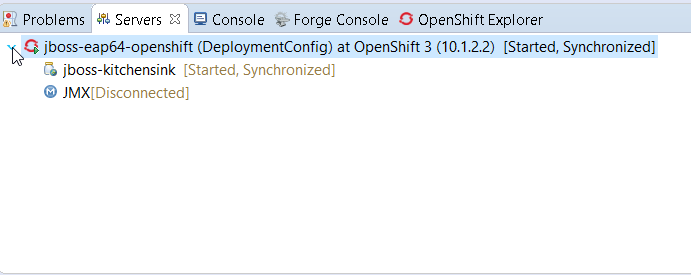
Once created, the kind of OpenShift resource adapter is also displayed in the Servers view:
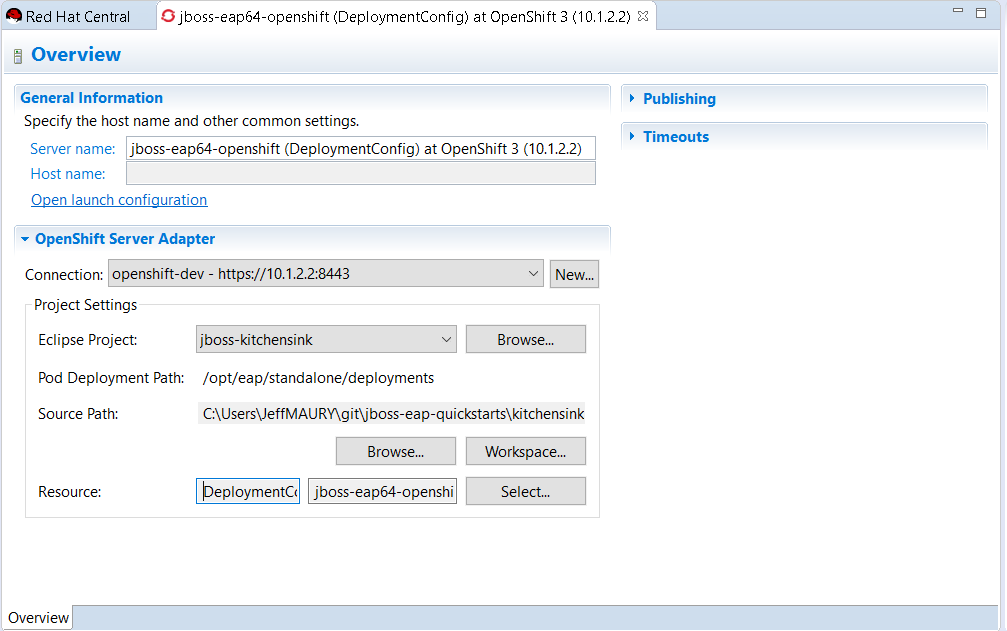
This information is also available from the server editor:
Related JIRA: JBIDE-23490
Pipeline builds support
Pipeline based builds are now supported by the OpenShift tooling. When creating an application, if using a template, if one of the builds is based on pipeline, you can view the detail of the pipeline:
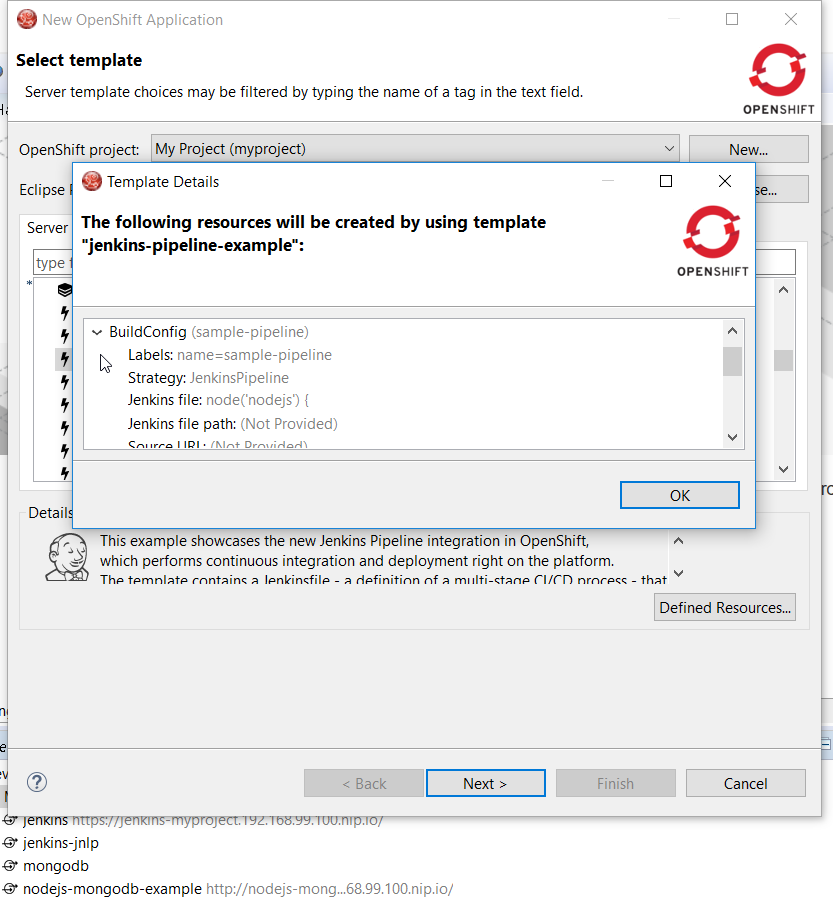
When your application is deployed, you can see the details of the build configuration for the pipeline based builds:
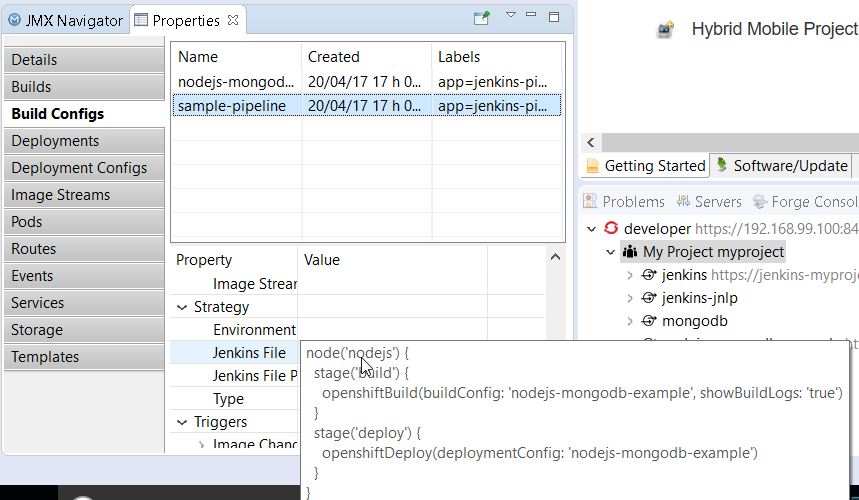
More to come as we are improving the pipeline support in the OpenShift tooling.
Related JIRA: JBIDE-24146
Security vulnerability fixed in certificate validation database
|
When you use the OpenShift tooling to connect to an OpenShift API server, the certificate of the OpenShift API server is first validated. If the issuer authority is a known one, then the connection is then established. If the issuer is an unknown one, a validation dialog is first shown to the user with the details of the OpenShift API server certificate as well as the details of the issuer authority. If the user accepts it, then the connection is established. There is also an option to store the certificate in a database so that next time a connection is attempted to the same OpenShift API server, then the certificate will be considered valid an no validation dialog will be show again. 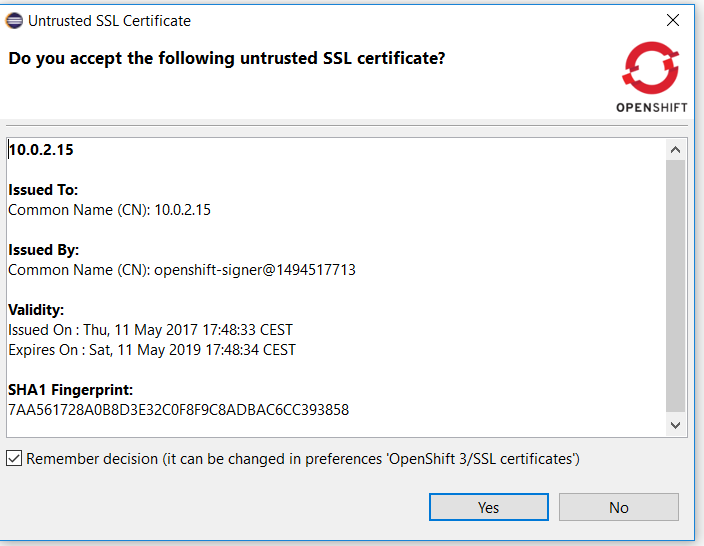
We found a security vulnerabilty as the certificate was wrongly stored: it was partially stored (not all attributes were stored) so we may interpret a different certificate as validated where it should not. We had to change the format of the certificate database. As the certificates stored in the previous database were not entirelly stored, there was no way to provide a migration path. As a result, after the upgrade, the certificate database will be empty. So if you had previously accepted some certificates, then you need to accept them again and fill the certificate database again. Related JIRA: JBIDE-24312 |
CDK 3 Server Adapter
The CDK 3 server adapter has been here for quite a long time. It used to be Tech Preview as CDK 3 was not officially released. It is now officiallly available. While the server adapter itself has limited functionality, it is able to start and stop the CDK virtual machine via its minishift binary. Simply hit Ctrl+3 (Cmd+3 on OSX) and type CDK, that will bring up a command to setup and/or launch the CDK server adapter. You should see the old CDK 2 server adapter along with the new CDK 3 one (labeled Red Hat Container Development Kit 3).
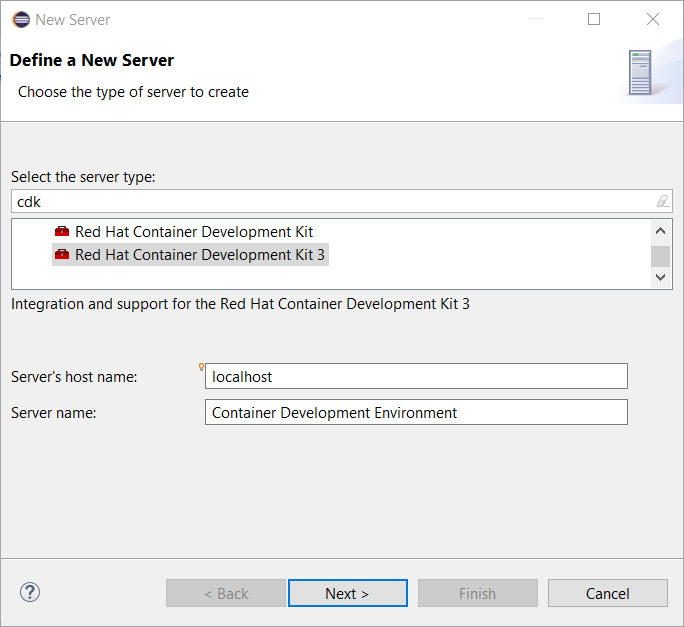
All you have to do is set the credentials for your Red Hat account and the location of the CDK’s minishift binary file and the type of virtualization hypervisor.
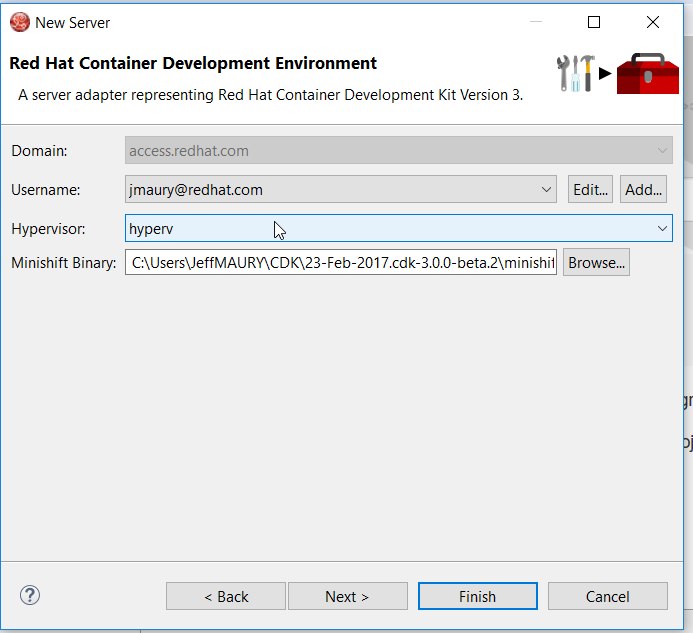
Once you’re finished, a new CDK Server adapter will then be created and visible in the Servers view.
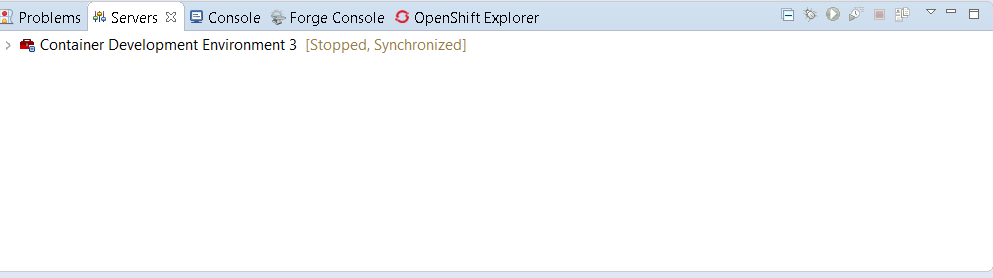
Once the server is started, Docker and OpenShift connections should appear in their respective views, allowing the user to quickly create a new Openshift application and begin developing their AwesomeApp in a highly-replicatable environment.
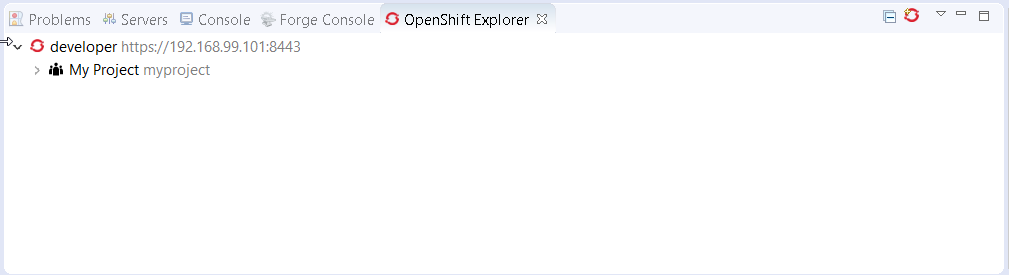
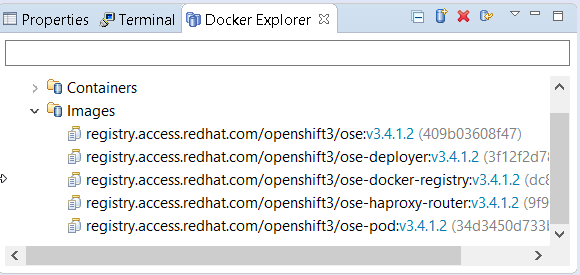
OpenShift Container Platform 3.5 support
OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) 3.5 has been announced by Red Hat. JBossTools 4.4.4.Final has been validated against OCP 3.5.
OpenShift server adapter extensibility
The OpenShift server adapter had long support for EAP/Wildfly and NodeJS based deployments. It turns out that it does a great deal of synchronizing local workspace changes to remote deployments on OpenShift which have been standardized through images metadata (labels). But each runtime has its own specific. As an example, Wildfly/EAP deployments requires that a re-deploy trigger is sent after the files have been synchronized.
In order to reduce the technical debt and allow support for other runtimes (lots of them in the microservice world), we have refactored the OpenShift server adapter so that each runtime specific is now isolated and that it will be easy and safe to add support for new runtime.
For a full in-depth description, see the following wiki page.
Server Tools
API Change in JMX UI’s New Connection Wizard
While hardly something most users will care about, extenders may need to be aware that the API for adding connection types to the 'New JMX Connection' wizard in the 'JMX Navigator' has changed. Specifically, the 'org.jboss.tools.jmx.ui.providerUI' extension point has been changed. While previously having a child element called 'wizardPage', it now requires a 'wizardFragment'.
A 'wizardFragment' is part of the 'TaskWizard' framework first used in WTP’s ServerTools, which has, for a many years, been used throughout JBossTools. This framework allows wizard workflows where the set of pages to be displayed can change based on what selections are made on previous pages.
This change was made as a direct result of a bug caused by the addition of the Jolokia connection type in which some standard workflows could no longer be completed.
This change only affects adopters and extenders, and should have no noticable change for the user, other than that the below bug has been fixed.
Related JIRA: JBIDE-24029 - Create JMX Connection wizard can not be finished when Jolokia plugin is activated
WildFly 11 Server Adapter
A server adapter has been added to work with WildFly 11. It’s currently released in Tech-Preview mode only, since the underlying WildFly 11 continues to be under active development with substantial opportunity for breaking changes.
WildFly 11 Incremental Management Deployment
JBoss Tools finally has support for incremental publishing commands issued over the management API to a running application server. Publishing over the management protocol has, in the past, always suffered from slow performance due to the requirement that the full deployment be sent over the wire on each change. In WildFly 11 and EAP 7.1, support for changes to individual files without having to send the entire deployment has been added.
Related JIRA: JBIDE-23784 - WF 11 / EAP 7.1 Incremental MGMT publishing